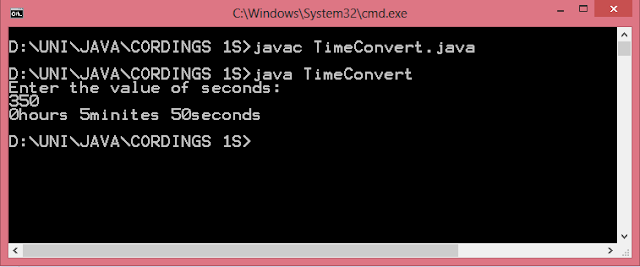
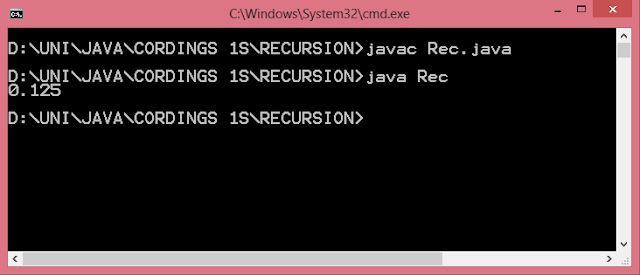
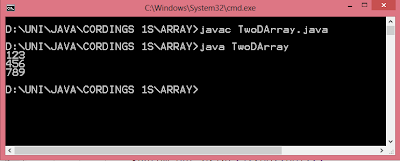
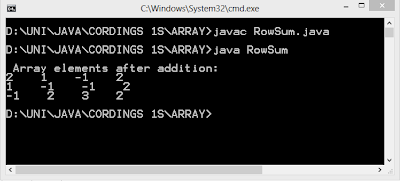
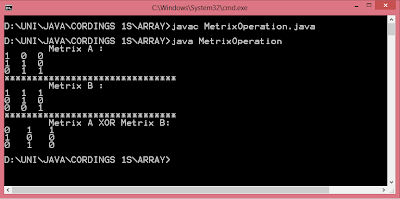
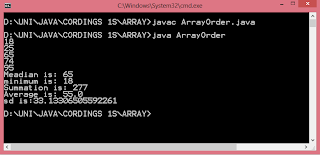
#include <GL/glut.h> int ww = 600, wh = 400; int first = 0; int xi, yi, xf, yf; void drawLine(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) { glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glLineWidth(5.0); glBegin(GL_LINES); glVertex2i(x1, y1); glVertex2i(x2, y2); glEnd(); glFlush(); } void display() { glClearColor(1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0); glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); glFlush(); } void mouse(int btn, int state, int x, int y) { if(btn==GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && state == GLUT_DOWN) { switch(first) { case 0: xi = x; yi = (wh-y); first = 1; break; case 1: xf = x; yf = (wh-y); drawLine(xi,yi,xf,yf); first = 0; break; } } } void myinit() { glViewport(0,0,ww,wh); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); gluOrtho2D(0.0,(GLdouble)ww,0.0,(GLdouble)wh); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); } int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutInit(&argc,argv); glutInitDisplayMode (GLU...